How to identify OXIDIZING & REDUCING agents in REDOX Reactions./ Steps, examples, and concept points/
Points To Recall
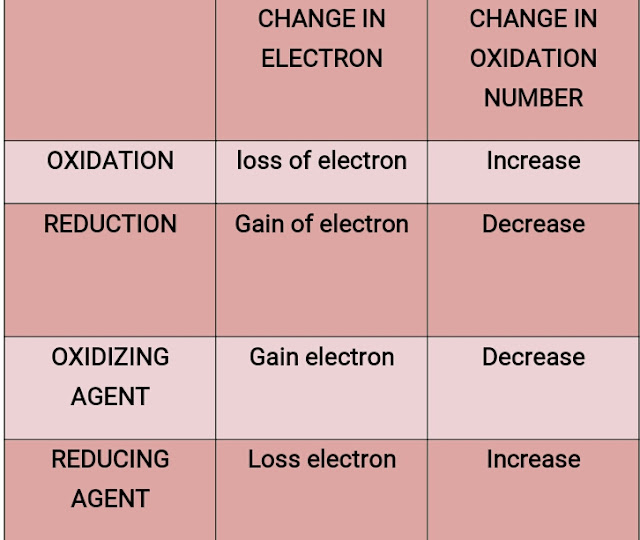
- Oxidation occurs by loss of electron/s and during oxidation process, oxidation number increases.
- Reduction occurs by gain of electron/s and in reduction process, oxidation number decreases.
- OXIDIZING agent cause oxidation in a reactant and get reduced during Redox reaction.
- REDUCING agent cause reduction in a reactant and get oxidized during Redox reaction.
As, REDOX Reactions occur with change in oxidation states/numbers of elements in reactants before and after reaction in reactants and products So, the key point in the identification of oxidizing and reducing agent is to have deep look at the change in the oxidation states of each element in reactants and products.
OXIDIZING and REDUCING agents' identification steps
- Determine oxidation states of each element in balanced chemical equation.
- Figure out elements which are changing their oxidation states in REDOX chemical equation at both side - in reactants and products.
- Element showing increase in oxidation state is getting oxidized- that reactant is reducing agent in REDOX Reactions.
- Element which is showing decrease in oxidation state is getting reduced- that is oxidizing agent.



Comments
Post a Comment
For any query you are always welcome. Feel free to contact me.